Raining Aliens?
Is It Raining Aliens?
Nearly 50 tons of mysterious red particles showered India in 2001. Now the race is on to figure out what the heck they are
By Jebediah Reed | June 2006
 | |
| Courtesy Dr. Godfrey Louis | |
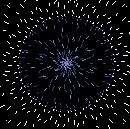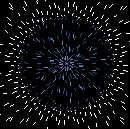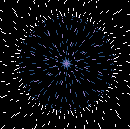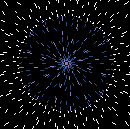
| E.T. Under the Microscope: Scientists have yet to identify the unusual particles [above, magnified 500 times] isolated from India’s mysterious red rainwater. | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 |
As bizarre as it may seem, the sample jars brimming with cloudy, reddish rainwater in Godfrey Louis’s laboratory in southern India may hold, well, aliens. In April, Louis, a solid-state physicist at Mahatma Gandhi University, published a paper in the prestigious peer-reviewed journal Astrophysics and Space Science in which he hypothesizes that the samples—water taken from the mysterious blood-colored showers that fell sporadically across Louis’s home state of Kerala in the summer of 2001—contain microbes from outer space.
Specifically, Louis has isolated strange, thick-walled, red-tinted cell-like structures about 10 microns in size. Stranger still, dozens of his experiments suggest that the particles may lack DNA yet still reproduce plentifully, even in water superheated to nearly 600˚F. (The known upper limit for life in water is about 250˚F.) So how to explain them? Louis speculates that the particles could be extraterrestrial bacteria adapted to the harsh conditions of space and that the microbes hitched a ride on a comet or meteorite that later broke apart in the upper atmosphere and mixed with rain clouds above India. If his theory proves correct, the cells would be the first confirmed evidence of alien life and, as such, could yield tantalizing new clues to the origins of life on Earth.
Meanwhile, more down-to-earth theories abound. One Indian government investigation conducted in 2001 lays blame for what some have called the “blood rains” on algae. Other theories have implicated fungal spores, red dust swept up from the Arabian peninsula, even a fine mist of blood cells produced by a meteor striking a high-flying flock of bats.
Louis and his colleagues dismiss all these theories, pointing to the fact that both algae and fungus possess DNA and that blood cells have thin walls and die quickly when exposed to water and air. More important, they argue, blood cells don’t replicate. “We’ve already got some stunning pictures—transmission electron micrographs—of these cells sliced in the middle,” Wickramasinghe says. “We see them budding, with little daughter cells inside the big cells.”




































































































0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home